15 April, 2025
What Are the Factors That Affect the Safety of PV Plants?
As the solar photovoltaic (PV) industry continues to expand rapidly, the installed capacity of PV power plants is increasing significantly, bringing heightened attention to safety issues. The safe operation of PV plants is crucial not only for maintaining power generation efficiency but also for ensuring equipment longevity and protecting investment returns. This article analyzes the key factors affecting PV plant safety from multiple perspectives.
1. Equipment Quality
Equipment quality forms the foundation for safe PV plant operation. Substandard equipment can create significant safety risks.
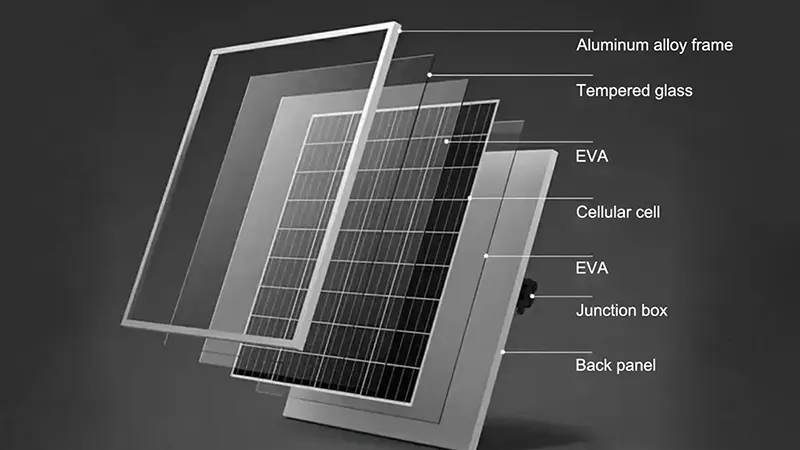
PV Module Quality
PV modules are the core of the system. High-quality modules offer better material selection, superior manufacturing, and encapsulation techniques, providing enhanced weather resistance, corrosion protection, and mechanical durability, thus reducing risks such as fire or physical damage.
Inverter Quality
Inverters are critical for converting solar energy into usable electricity. Their quality directly affects system performance and safety. Premium inverters are equipped with protections like overload and surge protection, while lower-end models may lack these features, introducing safety concerns.

Mounting Structures and Cable Quality
Mounting systems must offer structural integrity and corrosion resistance. PV cables must ensure high conductivity, insulation, and weatherproofing to prevent electrical faults or fire hazards.
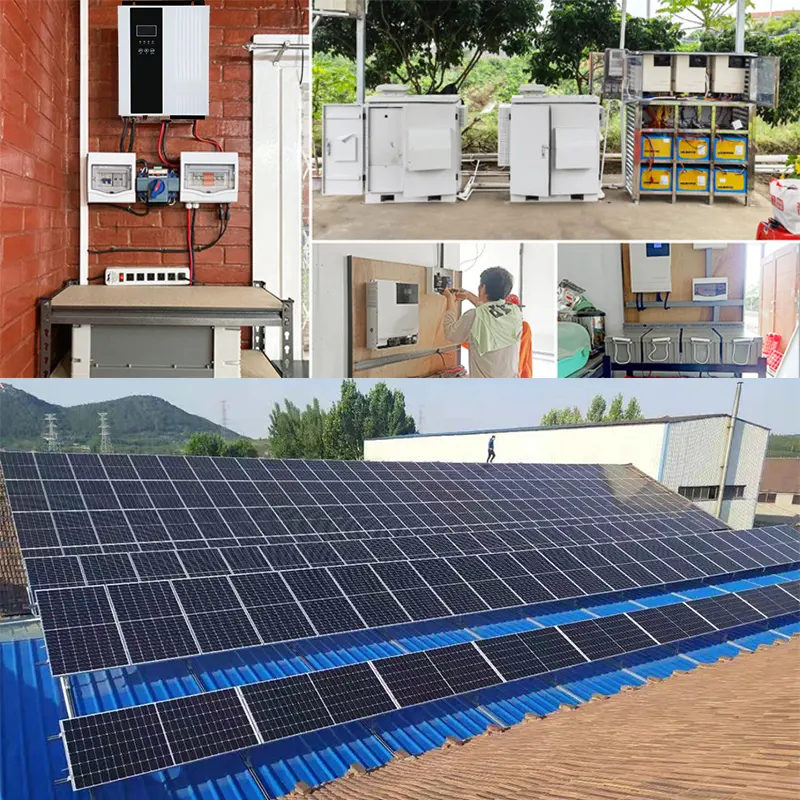
2.System Design and Installation
System design and installation directly impact the plant’s operational efficiency and safety.
Design Deficiencies
Poorly designed layouts can lead to shading issues, inadequate ventilation, or short circuits in the electrical system, reducing output and creating hazards.
Improper Installation
Improper installation may cause issues like faulty wiring or loose components, increasing the risk of fire or electric shock. For instance, improper grounding can result in serious safety incidents.
Mitigation Measures
Engage certified design and installation teams, strictly follow technical standards, ensure proper wiring and grounding, and implement lightning and fire protection measures. Conduct thorough testing and commissioning after installation to ensure system reliability.
3.Operation and Maintenance (O&M)
Proper O&M is key to the long-term safe operation of PV systems.

Lack of Preventive Maintenance
Without regular inspections, aging cables or loose connections may go unnoticed, leading to hidden dangers.
Inadequate Monitoring Systems
Lack of real-time monitoring makes it difficult to detect inverter faults or module anomalies in time.
Human Error
Operator errors may trigger short circuits or unexpected shutdowns, potentially damaging equipment.
Mitigation Measures
Establish standardized O&M procedures, perform routine inspections, address issues promptly, and conduct safety training for personnel.
4.Environmental Factors
PV plants are exposed to outdoor conditions and significantly affected by environmental factors.
Extreme Weather Conditions
Strong winds, hailstorms, or heavy rainfall can damage PV modules and support structures, disrupting safe operation.
Temperature Variations
High temperatures can accelerate component aging, while low temperatures may cause material brittleness
— both increasing failure risk.
Dust and Soiling
Dust, bird droppings, and other contaminants reduce energy output and may cause hotspots that lead to fire risks.
Mitigation Measures
Monitor weather patterns, implement emergency plans, perform regular cleaning, and conduct safety drills.
Safe and stable operation of PV plants is the cornerstone of efficient energy production and sustainable development. From equipment selection to design, installation, maintenance, and environmental adaptation, every aspect plays a vital role. Only through systematic risk identification, standard enhancement, and continuous oversight can we ensure reliable performance and accelerate the global transition to clean energy.
share