23 July, 2025
How to Choose Inverter for Solar Panel: 6 Essential Tips for Smart & Reliable Solar Systems
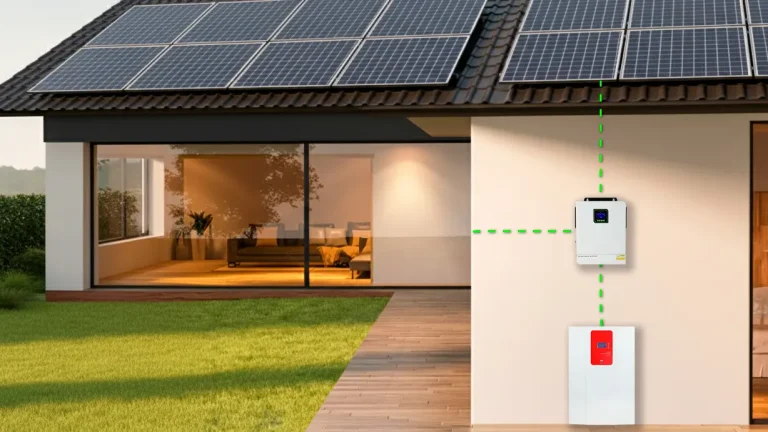
Whether used in off-grid systems or grid-connected generation, a solar PV system mainly consists of three core components: solar PV modules, a solar charge controller, and an inverter.
As a critical component, the inverter not only converts direct current (DC) into alternating current (AC) but also ensures that the output AC matches the grid’s voltage and frequency requirements, enabling efficient grid connection and stable power transmission.
Modern inverters also offer advanced features such as Maximum Power Point Tracking (MPPT), smart reactive power compensation, automatic grid re-connection, islanding detection, and arc fault protection. They support remote monitoring, string-level fault diagnosis, battery storage integration, home energy management, and intelligent air cooling systems—greatly enhancing safety and intelligence. These features make them ideal for both residential and commercial solar energy systems.
Choosing the Right Inverter Matters
Ensure Proper Equipment Operation
If the inverter capacity is too small, it may not support the startup or continuous operation of high-power appliances like air conditioners or refrigerators, causing frequent tripping or restarts. Conversely, an oversized inverter leads to wasted resources and inefficient operation under light loads, which can shorten its lifespan.
Maximize Energy Efficiency
A high-efficiency inverter minimizes energy loss during the DC-to-AC conversion process, thereby increasing the solar energy utilization rate and the overall power output of the system. Matching the inverter’s input voltage range to the system’s voltage also helps reduce compatibility-related energy losses.
Ensure System Safety and Stability
High-quality inverters typically come with multiple protection features such as overload, short-circuit, over-voltage, under-voltage, and over-temperature protection. These safeguards enable prompt shutdown during abnormal conditions to prevent equipment damage and ensure safety. For outdoor installations, inverters must be waterproof, dustproof, and moisture-resistant to withstand harsh weather.
Reduce Operating Costs
Choosing a properly sized and reliable inverter controls initial investment costs while ensuring long-term system performance. Reputable brands typically offer inverters with lifespans over 10 years and low failure rates, significantly reducing maintenance and replacement costs and avoiding downtime losses.
How to Choose the Right Inverter

Types of Solar Inverters
As a central component of solar systems, inverters are generally categorized by application and functionality into String Inverters, Micro Inverters, Hybrid Inverters, and Off-grid Inverters.
| Type | Application Scenario | Advantages | Disadvantages |
| String Inverter | Residential/Small Commercial | Low cost, easy maintenance | System performance is affected by weakest panel |
| Micro Inverter | Roof with shading/different angles | Each panel works independently, high efficiency | Higher cost |
| Hybrid Inverter | Grid + Storage | Battery support, flexible operation | Higher price, complex setup |
| Off-grid Inverter | Standalone Systems | Independent of grid, ideal for remote areas | Requires battery, more complex setup |
Choosing the right type of inverter is crucial for system performance and return on investment.
Inverter Sizing and System Capacity Matching
When designing a solar system, it is crucial to match the total capacity of the solar panels with the rated power of the inverter. This ratio, known as the DC/AC Ratio, is a key factor for measuring efficiency and return on investment.
A typical recommended DC/AC ratio ranges from 1.1 to 1.4, meaning the inverter capacity should be around 80%-90% of the total solar panel capacity.
Example: A 6kW solar panel array can be paired with a 5kW inverter, resulting in a DC/AC ratio of about 1.2.
Grid-Tied vs. Off-Grid
If your area has a stable and reliable power grid, a grid-tied inverter is the most common and cost-effective choice.
Grid-Tied inverter Advantages:
- Self-Consumption + Export: Solar energy powers household loads first; surplus energy is exported to the grid for credit or profit.
- No Battery Required: The grid acts as a virtual battery, reducing the need for battery storage.
- High Efficiency, Low Cost: Simple system structure, short payback period, and minimal maintenance.
- Net Metering Support: In many regions, excess energy sent to the grid is credited or subsidized under net metering programs.
For example, California (USA) supports NEM 3.0, where users are compensated for exported electricity based on time-of-use rates.
In Victoria, Australia, energy retailers must offer a minimum feed-in tariff of 3.3 AUD cents/kWh for exported solar electricity.
If you live in a remote area with limited grid access or wish to go completely off-grid, an off-grid inverter is the ideal solution.
Off-Grid inverter Advantages:
- Complete Energy Independence powered by solar panels and batteries.
- Requires Battery Storage to ensure uninterrupted power supply.
- Ideal for Remote Locations like farms, campsites, and off-grid buildings.
Hybrid Inverters
Hybrid inverters can operate in both grid-tied and off-grid modes and support battery storage, offering greater flexibility.
- Supports Battery + Grid Backup
- Seamless Grid-Outage Switching for uninterrupted power.
- Highly Compatible with unstable grids or regions prone to outages.
- Future-Proof and scalable for system upgrades.
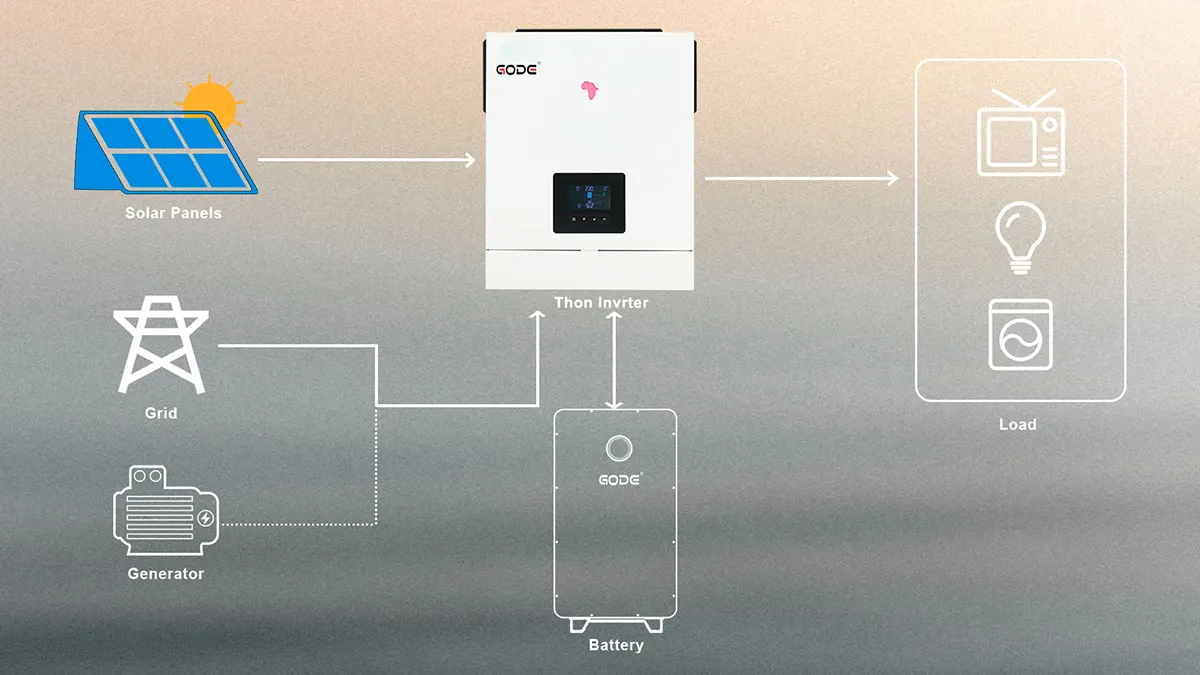
For example, the GODE THON series hybrid inverter supports PV, battery, and grid inputs, offering multiple operation modes including on-grid, off-grid, and anti-backflow control for smart energy management.
Efficiency
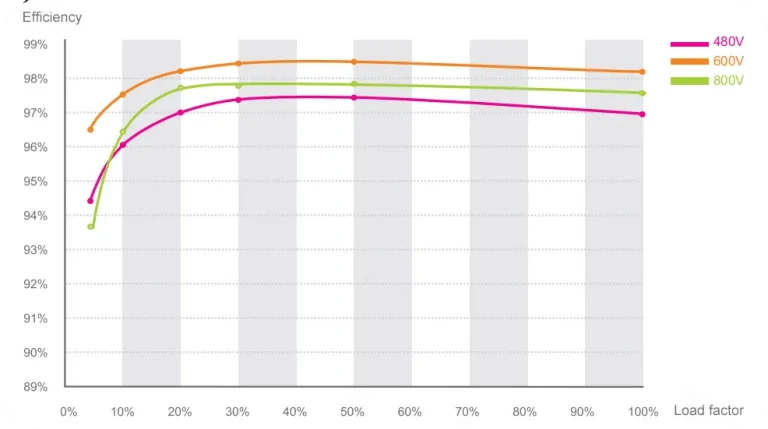
Inverter efficiency measures how much energy is lost during DC-to-AC conversion. Mainstream inverters usually achieve conversion efficiencies above 95%.
EURO Efficiency vs. Peak Efficiency
EURO Efficiency is the weighted average efficiency under various load conditions and better reflects real-world performance. Peak Efficiency is the maximum conversion efficiency under ideal conditions.
Understanding both metrics helps in selecting an inverter that optimizes real-world energy production.
Brands and Warranty
When selecting an inverter, brand and warranty are critical. Top international brands ensure stable quality, reliable performance, and comprehensive support. Recommended brands include SMA, Fronius, Growatt, Huawei, GODE.
To explore key highlights, product strengths, and why these brands are leading the market, check out our full guide on the Top 10 Solar Inverters in the World.
GODE inverters come with 5 to 10 years of warranty, with optional extended coverage, ensuring long-term stability and minimal maintenance risks.
Compatibility and Smart Features
Modern inverters should not only handle basic power conversion, but also support smart features to enhance user experience and system management.
Key Features Include:
Battery Expandability: Support for connecting storage batteries to enable energy backup and self-consumption.
Built-in WiFi & Remote Monitoring: Allows real-time monitoring, fault alerts, and system control via a mobile app or web interface.
For example, the GODE STM series hybrid inverters support battery expansion and remote monitoring, enabling intelligent energy management and high operational efficiency.
Common Mistakes When Choosing Inverters
Ignoring Inverter and Grid Voltage Compatibility
Grid voltage and frequency vary by region—Europe uses 230V, 50Hz; the US uses 120/240V, 60Hz.
Always verify whether your system connects to a single-phase or three-phase grid. Commercial/industrial users typically operate on 380V–415V three-phase power (L1, L2, L3 + N).
Overlooking voltage compatibility can lead to startup failures, error codes, or even hardware damage.
Using Non-Certified or Non-Compliant Models
Your inverter must comply with local safety certifications and standards (e.g., CE, UL, CSA). Non-compliant devices may pose legal risks and safety concerns.
Oversizing or Undersizing the Inverter
Mismatch between inverter size and panel capacity reduces overall efficiency. Undersized inverters fail to meet load requirements; oversized ones waste energy and reduce efficiency at low loads.
Final Thoughts
Choosing the right inverter is essential for building a safe, efficient, and long-lasting solar power system. Key factors to consider include the system size and proper sizing (DC/AC ratio), the intended application (grid-tied, off-grid, or hybrid), brand reputation and relevant certifications, smart features such as remote monitoring, compatibility with local voltage and frequency standards, and the warranty and support provided by the manufacturer. A well-matched inverter not only enhances energy output and system stability but also reduces long-term maintenance costs and maximizes return on investment.
The right inverter improves energy yield, reduces maintenance costs, and maximizes return on investment.
share