16 April, 2025
Micro-Inverter V String Inverter
Inverters are essential components of solar photovoltaic (PV) systems. Their primary function is to convert the direct current (DC) generated by solar panels into alternating current (AC) that can be used for homes, businesses, or fed into the grid.
In addition, inverters perform vital functions such as system monitoring, Maximum Power Point Tracking (MPPT), and safety protection.
Inverters can be classified based on their connection structure into central inverters, string inverters, and micro-inverters. For residential or small commercial solar installations, choosing between a string inverter and a micro-inverter can be challenging. This article compares both types in terms of definition and application scenarios.
Definition
String Inverter
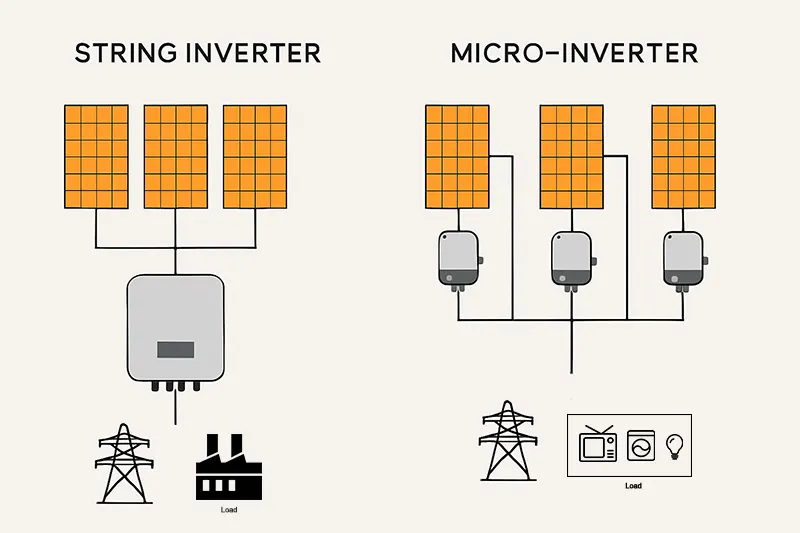
A string inverter connects multiple solar panels in series to form a “string” and uses a single inverter to convert the DC electricity into AC. It is suitable for large rooftops with uniform orientation and minimal shading.
Micro-Inverter
A micro-inverter is a compact inverter installed on the back of each individual solar panel. It converts DC to AC per panel, and all outputs are combined as AC before connecting to the grid.
This configuration allows each panel to operate independently, significantly increasing system efficiency — especially in cases with shading or complex roof designs.
Application Scenarios
String Inverter
String inverters are widely used in residential, commercial, and industrial-scale solar systems. Key application scenarios include:
1. Unshaded, large-area rooftops
Commercial buildings, factories, schools, logistics parks, supermarkets
Sufficient roof space with consistent orientation
Solar panels receive uniform sunlight
2. Ground-mounted solar farms or utility-scale projects
Centralized inverter layout
Standardized grid-connection setups
3. Budget-limited projects
Cost-sensitive investors
Basic system performance requirements
Micro-Inverter
Micro-inverters are better suited for complex roof structures and high-end residential applications. Key use cases include:
1. Roofs with partial shading
Each panel generates power independently
Shading on one panel does not affect the whole system
2. Multi-angled or non-uniform rooftop installations
Panels facing different directions
Micro-inverters support individual MPPT, optimizing output
3. Premium residential or hybrid solar + storage systems
High precision, detailed performance monitoring
Intelligent operation and better long-term yield
How to Choose
String inverters are ideal for standardized, cost-sensitive medium to large projects, offering high cost-performance but requiring consistent environmental conditions.
Micro-inverters are more suitable for users prioritizing efficiency, flexibility, and high-performance monitoring, especially on complex rooftops or in long-term investment scenarios.
share