22 September, 2025
What Is Meant by Peak Shaving
Peak shaving is an essential strategy in modern energy management that helps businesses and large consumers optimize their electricity usage, reduce costs, and support grid stability. With the rise of renewable energy integration and smart grid technologies, understanding and implementing peak shaving is becoming increasingly critical.
What is Peak Shaving
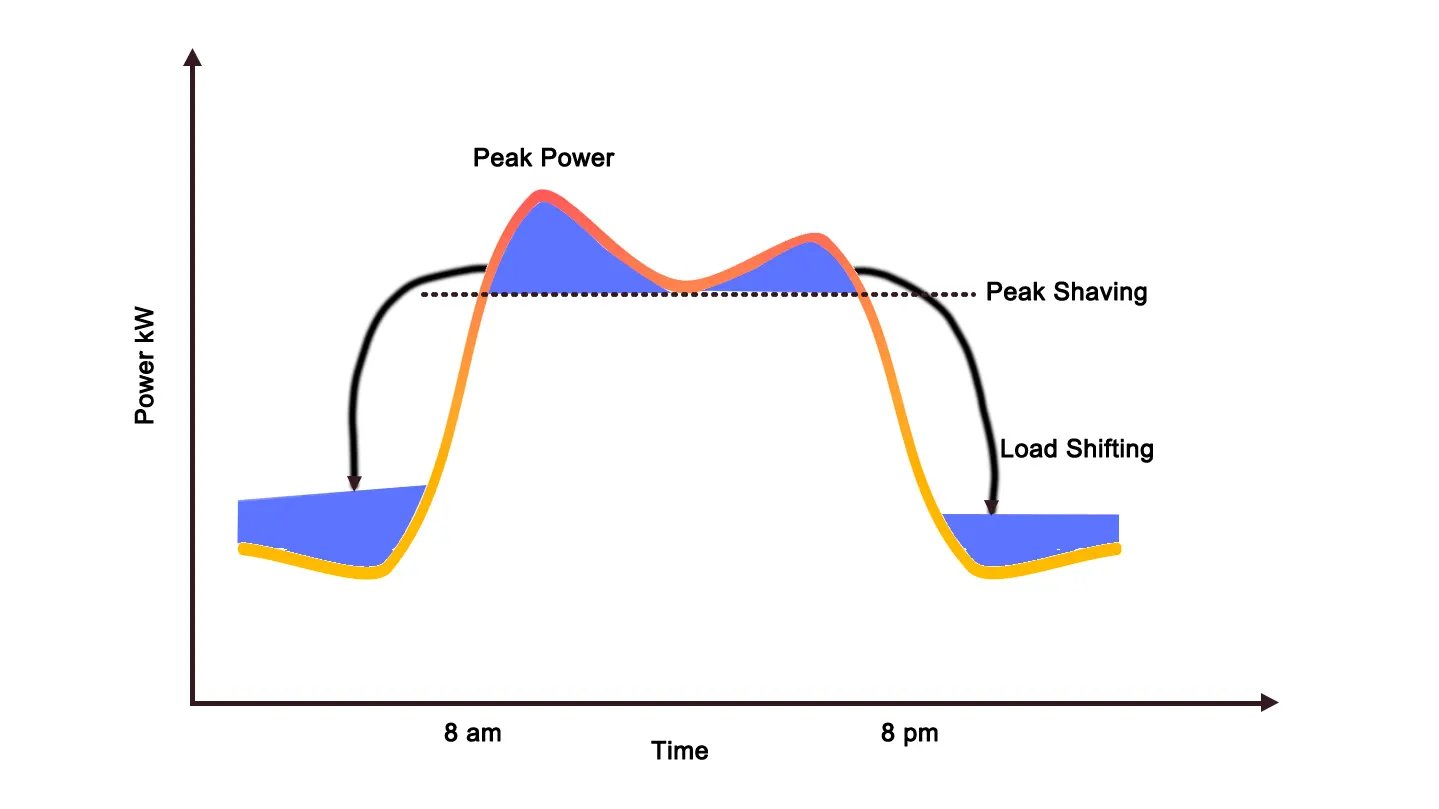
In power systems, peak shaving refers to reducing electricity demand during peak periods by adjusting user loads to balance the grid. Common methods include encouraging users to shift consumption to off-peak hours and limiting high-energy-consuming equipment, thereby alleviating peak stress and improving supply stability.
For businesses and large energy users, peak shaving has a direct financial impact. By minimizing peak electricity demand, companies can effectively reduce energy costs, making peak shaving an effective cost-saving strategy.
How Peak Shaving Works
Peak shaving can be implemented through demand-side management, supply-side management, and intelligent control systems.
Demand-Side Management and Incentives
The goal of demand-side management is to reduce electricity demand during peak hours through a variety of strategies:
- Residential users: Use time-of-use pricing to encourage off-peak electricity consumption;
- EV users: Lower nighttime charging prices to guide charging behavior;
- Industrial users: Limit non-essential high-power equipment during peak periods to reduce unnecessary load.
Supply-Side Management
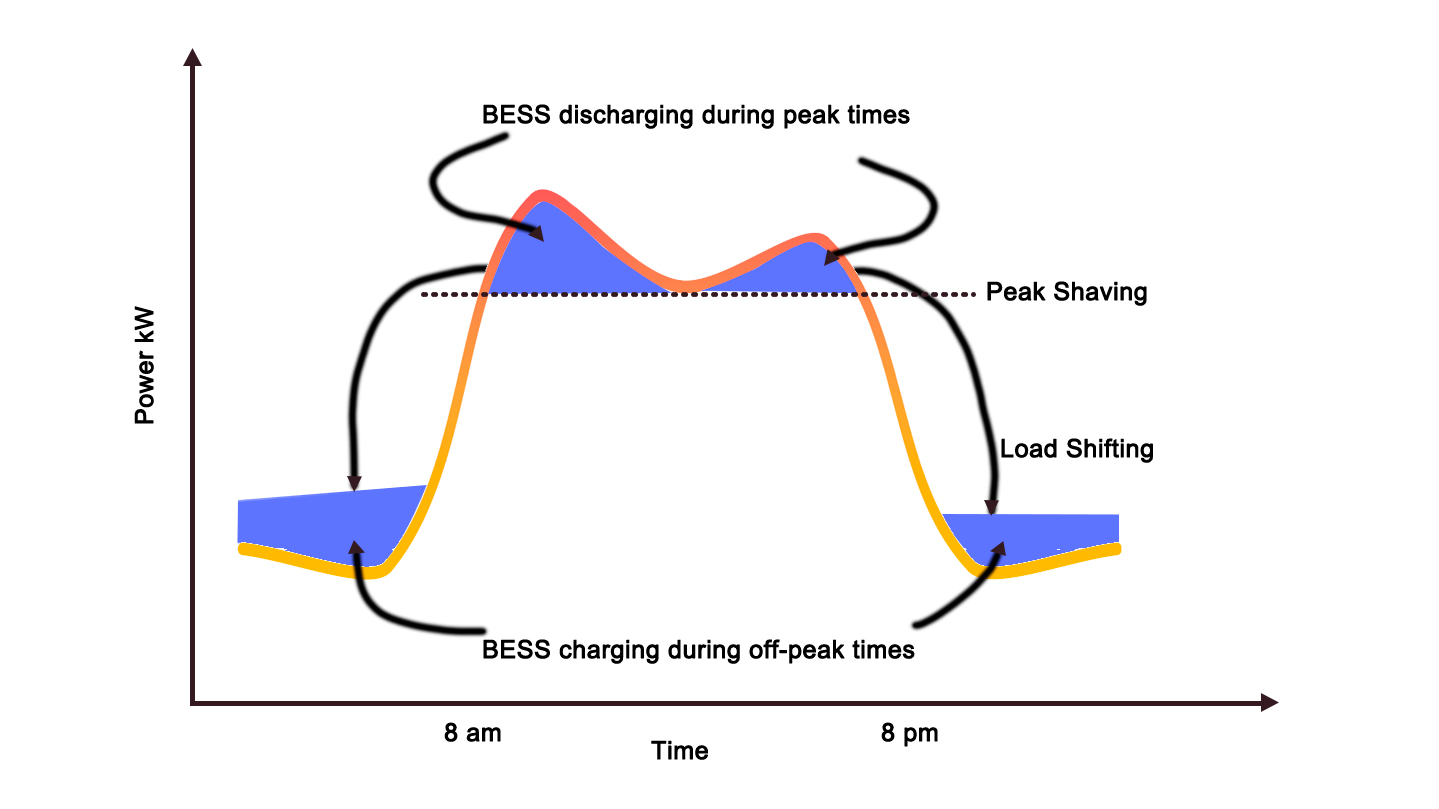
Supply-side management mainly relies on energy storage and power generation equipment regulation:
- During off-peak periods, energy storage systems charge using low-cost electricity and discharge during peak periods to relieve grid stress;
- Combine with PV and gas generators to prioritize efficient, clean generation for base load and activate backup or peaking units during peak hours.
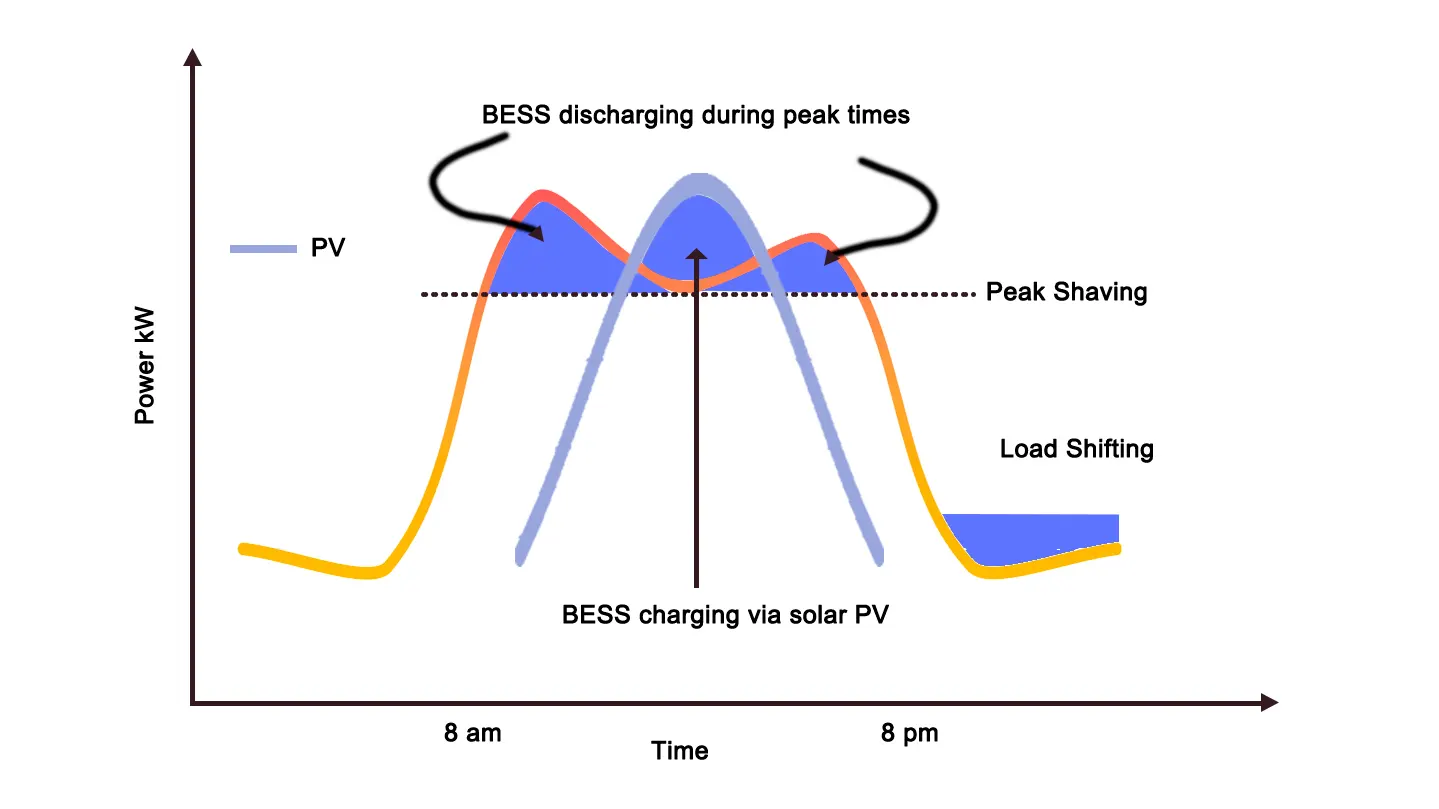
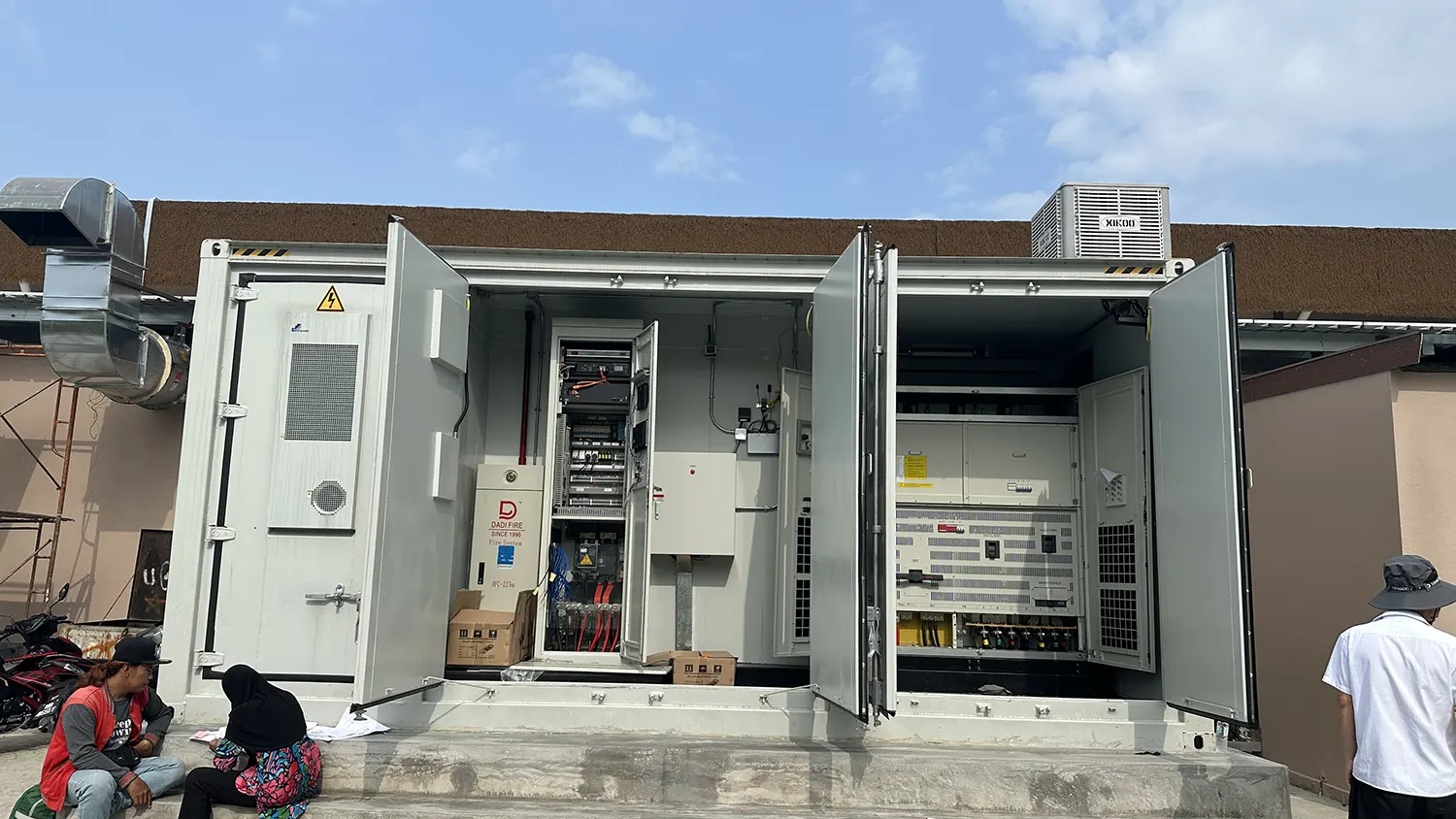
The Dino Desert project in Malaysia used GODE’s 1MW energy storage system to not only effectively reduce electricity peaks and costs, but also achieve more flexible energy scheduling.

Intelligent Control System Coordination
Smart grid technology monitors grid load, generation output, and storage status in real time. Algorithms automatically control energy storage and generator operation to achieve dynamic supply-demand balance.
Benefits of Peak Shaving
Reduce Grid Costs
In many regions, grid fees are not only based on energy consumption but also peak demand. In Germany, large users pay basic and energy charges plus a capacity charge linked to peak demand. A 15-minute peak can influence annual costs.
Advanced peak shaving algorithms predict and dynamically optimize loads to avoid unnecessary peak fees while maximizing self-consumption and energy flexibility.
Enhance Grid Stability
In 2024, extreme heat in China’s Sichuan-Chongqing region led to record grid loads. Transferring 10% of peak demand (~5 GW) through peak shaving and valley filling could prevent power outages for 3 million users.
Promote Renewable Energy Integration
Peak shaving supports carbon reduction and clean energy use. Energy storage and load transfer can absorb more wind and PV generation, reducing 6%-8% curtailment. Each 100 GWh of peak load shifted saves ~30,000 tons of standard coal and reduces CO₂ emissions by ~80,000 tons.
Economic Benefits Example
A key reason businesses and large users prioritize peak shaving is its measurable economic benefits.
In many regions, grid fees are linked not only to energy consumption but also to peak demand. In other words, a single peak within a billing period can significantly impact costs.
Example:
- A factory with 5 MW peak demand pays $100/kW/year in capacity charges;
- Reducing 1 MW peak lowers annual grid costs from $500,000 to $400,000;
- Saving $100,000 per year.
| Scenario | Peak Load | Capacity Rate | Annual Cost | Savings |
| No Peak Shaving | 5 MW | $100/kW/year | $500,000 | – |
| Peak Shaving 1 MW | 4 MW | $100/kW/year | $400,000 | $100,000 |
This example highlights the value of load management: even a partial reduction of peak demand can generate substantial cost savings. For EV charging hubs, data centers, or high-energy manufacturing, peak shaving can result in hundreds of thousands or even millions of dollars in annual savings.
Future Trends of Peak Shaving
Peak shaving is not merely a technical measure within power systems; it is also a strategic tool for corporate energy management and green transformation. With the advancement of digitalization and intelligence in energy systems, the potential of peak shaving will be further unleashed.
- Smart Grid: Enhanced real-time monitoring and scheduling enables precise load management;
- AI Forecasting: Utilize big data and AI to improve demand and renewable output predictions, planning peak shaving strategies in advance;
- Blockchain Energy Trading: Facilitate peer-to-peer energy transactions and virtual power plant coordination for flexible cross-user load management.
Businesses implementing peak shaving strategies early can reduce costs, increase revenue, and gain a competitive edge in the low-carbon economy.
Peak Shaving FAQs
share