Was ist eine Batterie-AC-Kopplung?
Mit der zunehmenden Verbreitung von Energiespeichersystemen in privaten, gewerblichen und industriellen Anwendungen beschäftigen sich immer mehr Nutzer mit einer scheinbar einfachen, aber entscheidenden Frage: Wie genau wird eine Batterie in ein Solarenergiesystem integriert?
In realen Projekten ist eine Batterie nicht etwas, das man einfach “einstecken und benutzen” kann. Die Art und Weise, wie sie mit Solarmodulen, Wechselrichtern und dem Stromnetz verbunden ist, wirkt sich direkt auf die Flexibilität des Systems, die Gesamteffizienz und die Möglichkeit einer zukünftigen Erweiterung aus. Unter den verfügbaren Architekturen ist die Batterie-AC-Kopplung heute eine der am weitesten verbreiteten und allgemein akzeptierten Lösungen.
Die AC-Kopplung definiert, ob die Batterie auf der AC- oder der DC-Seite des Systems angeschlossen ist und wie die elektrische Energie während des Ladens und Entladens umgewandelt wird. Das Verständnis dieses Konzepts hilft nicht nur bei der Entscheidung, ob die AC-Kopplung für Ihr Projekt geeignet ist, sondern ermöglicht auch einen fundierteren Vergleich zwischen AC- und DC-Kopplung.
In den folgenden Abschnitten erläutern wir, was die Batterie-Wechselstrom-Kopplung ist, wie sie funktioniert, wie sie sich von der Gleichstrom-Kopplung unterscheidet und für welche Anwendungen sie am besten geeignet ist, damit Sie eine klarere und zuverlässigere Entscheidung treffen können.
Was ist eine Batterie-AC-Kopplung?
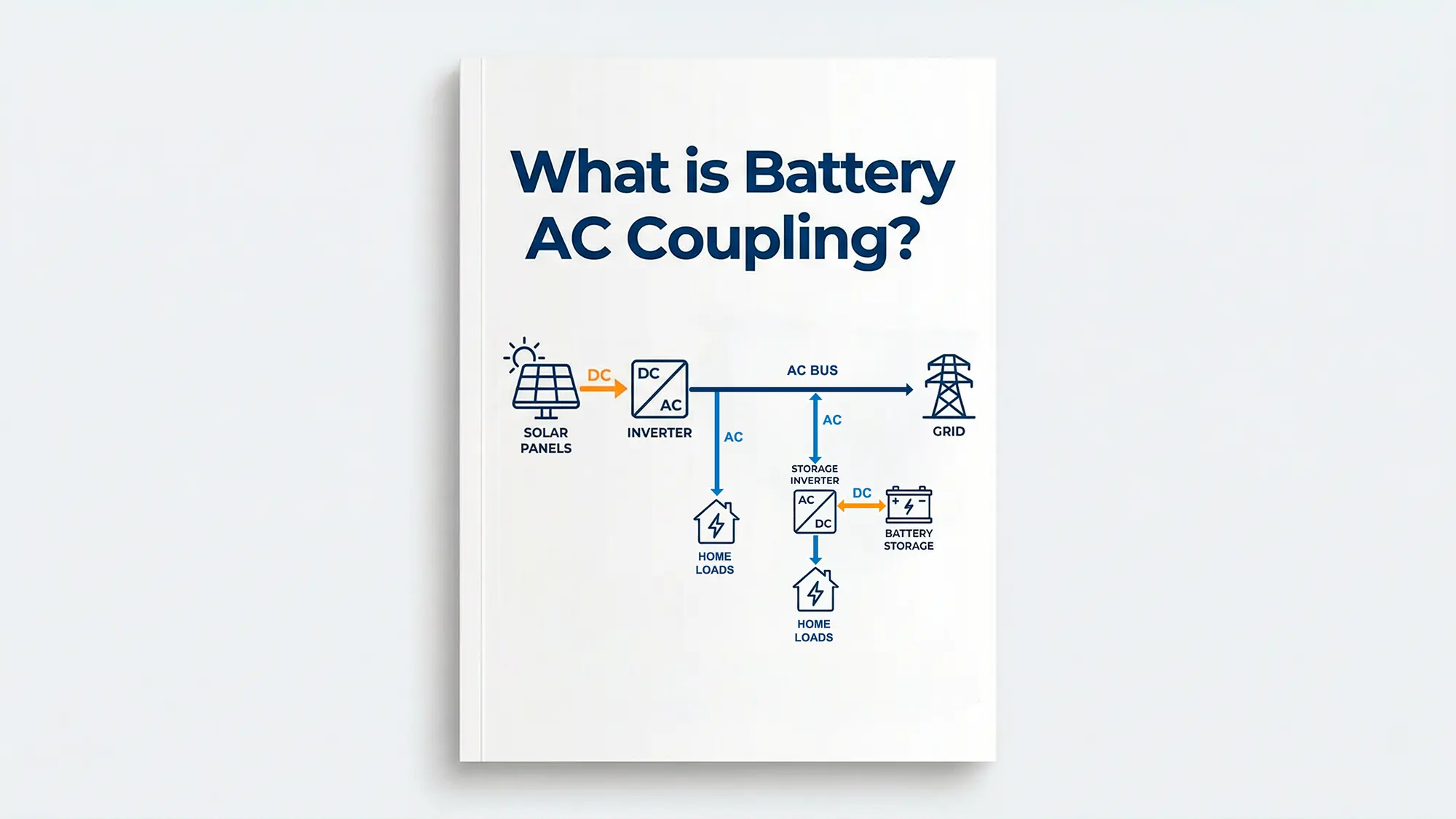
Die Batterie-AC-Kopplung bezieht sich auf eine Systemarchitektur, bei der die Batterie über einen speziellen Energiespeicher-Wechselrichter an die AC-Seite eines Solar- oder Stromsystems angeschlossen ist.
Vereinfacht gesagt, arbeiten die Photovoltaikanlage und das Energiespeichersystem unabhängig voneinander, sind aber an denselben Wechselstrombus angeschlossen. Die Batterie ist nicht direkt mit der Gleichstromseite der Solarmodule verbunden, sondern lädt und entlädt sich über Wechselstrom.
Aufgrund dieser “entkoppelten” Architektur ist die AC-Kopplung besonders häufig bei Anwendungen anzutreffen, die eine hohe Systemflexibilität erfordern, insbesondere wenn Batterien zu einem späteren Zeitpunkt zu einer bestehenden Solaranlage hinzugefügt werden.
Wie funktioniert die Batterie-AC-Kopplung?
Um zu verstehen, wie die Wechselstromkopplung funktioniert, muss man im Wesentlichen den Stromfluss durch das System verfolgen, der sich in den Lade- und den Entladevorgang unterteilen lässt.
Prozess der Aufladung
a) Der von Solarmodulen oder anderen Gleichstromquellen erzeugte Gleichstrom wird zunächst durch den PV-Wechselrichter in Wechselstrom umgewandelt.
b) Der umgewandelte Wechselstrom fließt in den AC-Bus und wird zunächst zur Versorgung lokaler Lasten verwendet, um den Strombedarf in Echtzeit zu decken.
c) Wenn auf dem AC-Bus überschüssige Energie vorhanden ist, wird der überschüssige AC-Strom vom Energiespeicher-Wechselrichter in Gleichstrom umgewandelt und in der Batterie gespeichert.
Entladungsprozess
a) Wenn Batteriestrom benötigt wird, wird der in der Batterie gespeicherte Gleichstrom durch den Speicherwechselrichter in Wechselstrom umgewandelt (DC→AC).
b) Der umgewandelte Wechselstrom kann dann direkt an lokale Verbraucher geliefert oder in das Netz zur Stromversorgung oder zum Energiehandel eingespeist werden.
Durch diese Koordinierung wird eine bidirektionale Umwandlung zwischen Gleich- und Wechselstrom erreicht, so dass sich die Batterie nahtlos an Wechselstromnetze oder Wechselstromlasten anschließen und flexible Lade- und Entladevorgänge durchführen kann.
Vor- und Nachteile der Batterie-AC-Kopplung
Wie jede Systemarchitektur hat auch die AC-Kopplung sowohl Vorteile als auch Grenzen, die auf der Grundlage spezifischer Anwendungsszenarien bewertet werden sollten.
Vorteile
Hohe Flexibilität
Das Energiespeichersystem arbeitet parallel zur PV-Anlage oder zum Netz auf der Wechselstromseite und ermöglicht sowohl einen unabhängigen als auch einen koordinierten Betrieb. Im Falle eines Netzausfalls kann das System schnell in den netzunabhängigen Modus wechseln, um kritische Verbraucher mit Strom zu versorgen.
Starke Kompatibilität
AC-gekoppelte Systeme lassen sich nahtlos in bestehende Wechselstromnetze oder -anlagen integrieren, wobei in der Regel keine größeren Systemänderungen erforderlich sind. Sie unterstützen Kombinationen von PV-Wechselrichtern und Speichergeräten verschiedener Marken und Modelle.
Ausgezeichnete Skalierbarkeit
Die AC-Kopplung ist ideal für die Ergänzung bestehender PV-Anlagen durch Batterien. Sie ist nicht durch die Nennleistung eines einzelnen Geräts eingeschränkt und ermöglicht eine schrittweise Erweiterung der Solarkapazität oder des Batteriespeichers zur Deckung des künftigen Energiebedarfs.
Benachteiligungen
Relativ geringere Energieeffizienz
Solarenergie muss zwei Umwandlungen durchlaufen - DC→AC→DC - bevor sie in der Batterie gespeichert wird. Jede Umwandlung ist mit Verlusten verbunden, die sich in geringerer Gesamtwirkungsgrad im Vergleich zu DC-gekoppelten Systemen.
Höhere Hardwarekosten
Ein zusätzlicher Wechselrichter zur Energiespeicherung ist erforderlich, was die Gesamtkosten der Anlage erhöht.
Größerer Platzbedarf
Mehr Geräte führen zu einem größeren Platzbedarf und stellen höhere Anforderungen an die Standortbedingungen und das Systemlayout.
Der Hauptvorteil von AC-gekoppelten Solarbatteriesystemen liegt in der einfachen Installation und den relativ geringen Anfangsinvestitionen.
Darüber hinaus kann die Batterie bei AC-gekoppelten Systemen sowohl von den Solarzellen als auch vom Stromnetz geladen werden. Selbst wenn die Solarstromerzeugung unzureichend ist, kann die Batterie über das Netz geladen werden, was die Gesamtverfügbarkeit des Systems verbessert.
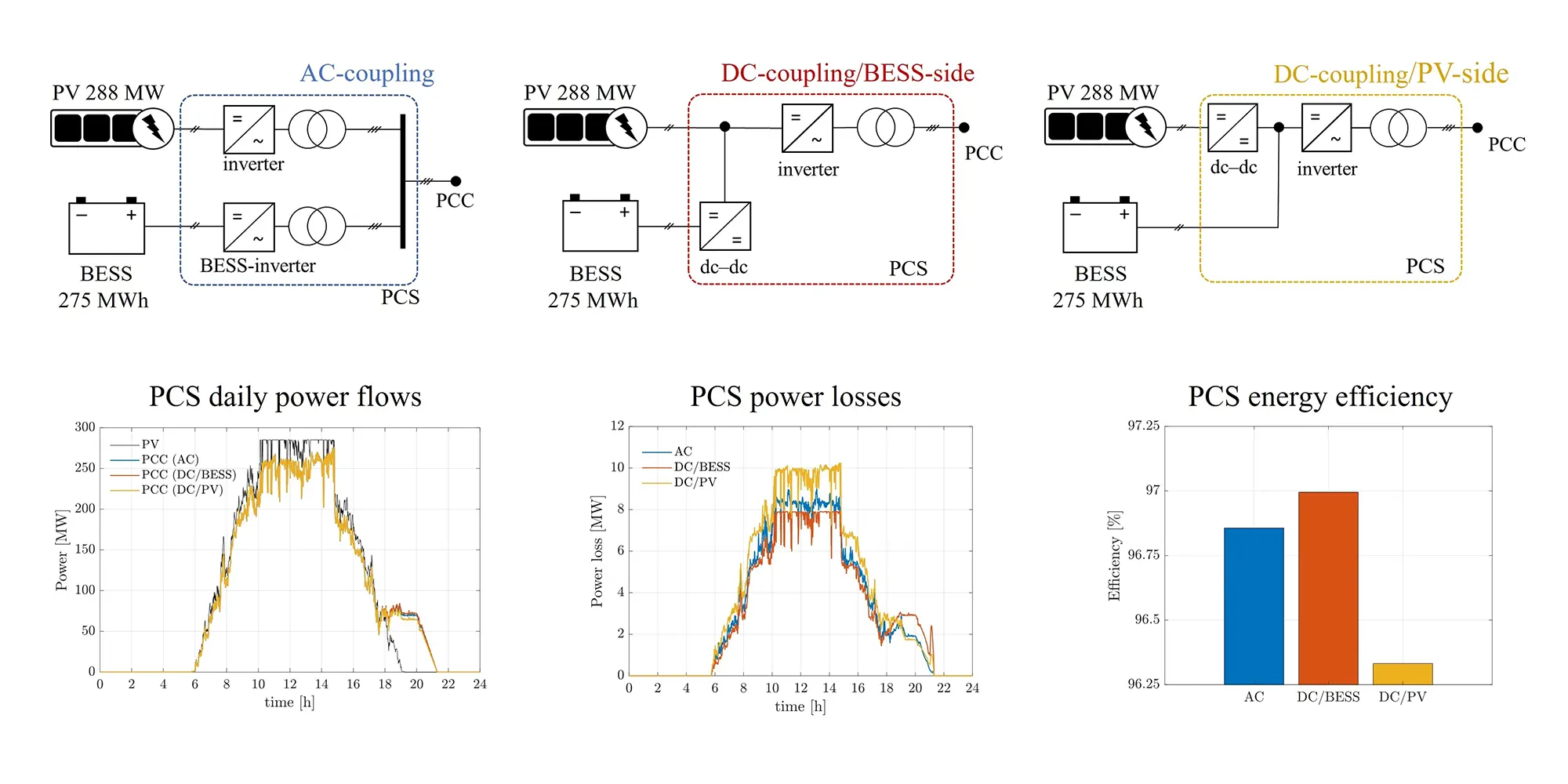
AC-Kopplung vs. DC-Kopplung
In gleichstromgekoppelten Systemen fließt der Gleichstrom von den Solarmodulen direkt zum Wechselrichter des Speichers. Ein Teil des Stroms wird in Wechselstrom für lokale Verbraucher oder die Netzeinspeisung umgewandelt, während der verbleibende Teil die Batterie direkt oder über einen DC-DC-Wandler lädt.
| Vergleich Artikel | AC-Kupplung | DC-Kopplung |
| Energieumwandlungspfad | DC → AC → DC | DC → DC |
| Effizienz des Systems | Etwas niedriger | Höher |
| Komplexität der Installation | Einfacher, insbesondere für bestehende PV-Anlagen | Komplexer, insbesondere bei Nachrüstungen |
| Konfiguration des Wechselrichters | PV-Wechselrichter + Speicherwechselrichter | Speicher-Wechselrichter |
| Flexibilität des Systems | Hohe, starke Mehrmarken-Kompatibilität | Niedrigere, höhere Anforderungen an die Systemanpassung |
| Typische Anwendungen | Nachrüstung von Batterien, schrittweiser Ausbau | Neue Projekte mit Schwerpunkt auf hoher Effizienz |
Insgesamt ist die AC-Kupplung ideal für Nachrüstungen und flexible Systeme, während die DC-Kupplung besser für Neuinstallationen geeignet ist, bei denen es auf maximale Systemeffizienz ankommt.
Unabhängig davon, ob es sich um DC- oder AC-gekoppelte Systeme handelt, dient der Wechselrichter zur Energiespeicherung oft als Kernkomponente des gesamten Systems. Er spielt eine entscheidende Rolle bei der Koordinierung von Solarstromerzeugung, Batteriespeicherung und Netzinteraktion und bestimmt gleichzeitig die Effizienz, Zuverlässigkeit und Skalierbarkeit des Gesamtsystems.
Die Solarspeicher-Wechselrichter der THon-Serie sind für Energiespeicheranwendungen in Privathaushalten und kleinen Gewerbebetrieben konzipiert und bieten flexible Unterstützung für Netzstrom, PV-Solaranlagen und die Integration von Batterien in einer Vielzahl von Systemkonfigurationen.
Die Serie unterstützt den Parallelbetrieb von bis zu sechs Einheiten, so dass die Systemkapazität bei wachsenden Projektanforderungen erweitert werden kann. Mit einem MPPT-Wirkungsgrad von bis zu 99% gewährleistet sie eine effiziente Energiegewinnung auch bei wechselnden Sonnenbedingungen. Ob in neuen hybriden Energiesystemen oder als Kernkomponente für System-Upgrades und Nachrüstungen - die THon-Serie sorgt für ein ausgewogenes Verhältnis zwischen Leistung, Zuverlässigkeit und zukünftiger Erweiterbarkeit.
Wann sollten Sie sich für ein batteriebetriebenes AC-gekoppeltes System entscheiden?
Hinzufügen eines Speichers zu einem bestehenden PV-System
Für Nutzer, die bereits eine PV-Anlage haben und später einen Energiespeicher hinzufügen möchten, ist die AC-Kopplung in der Regel die bessere Option, da sie komplexe Systemänderungen vermeidet.
Künftige Expansionspläne
In AC-gekoppelten Systemen sind die PV-Anlage und das Speichersystem relativ unabhängig, so dass die Kapazität auf der AC-Seite je nach Bedarf erweitert werden kann.
Multi-Energie-Integrationsszenarien
Wenn mehrere Energiequellen wie Solar- und Windenergie sowie das Versorgungsnetz integriert werden müssen, ermöglicht die AC-Kopplung eine effektivere Koordination der Energieein- und -ausgänge im Rahmen eines einheitlichen Energiemanagementsystems.
Hohe Anforderungen an die Kompatibilität der Geräte
AC-gekoppelte Systeme bieten eine größere Kompatibilität zwischen verschiedenen Gerätemarken und -modellen.
Schlussfolgerung
Insgesamt bieten batteriegestützte AC-gekoppelte Systeme klare Vorteile bei Nachrüstungsprojekten, Kapazitätserweiterungen, Multi-Energie-Integration und Anwendungen, die eine hohe Flexibilität erfordern. Ihre Energieeffizienz ist zwar etwas geringer als die von DC-gekoppelten Systemen, aber ihre einfache Installation, starke Kompatibilität und hervorragende Erweiterbarkeit machen sie zu einer ausgereiften und zuverlässigen Wahl für moderne Energiespeicherprojekte.
Bei der Auswahl einer Systemarchitektur empfiehlt es sich, die vorhandenen Systembedingungen, die Budgetbeschränkungen und die langfristige Planung zu bewerten, um die am besten geeignete Energiespeicherlösung zu ermitteln.
Aktie