agosto 26, 2025
O guia completo para a capacidade da bateria
Quando escolhemos uma central eléctrica portátil ou uma bateria solar, deparamo-nos com a mesma questão: de quanta capacidade de bateria necessitam realmente?
A capacidade da bateria não só determina a quantidade de energia que pode ser armazenada, como também afecta diretamente o tempo que pode alimentar os seus dispositivos. Quer se trate de campismo ao ar livre, de reserva de emergência em casa ou de energia móvel diária, compreender a capacidade da bateria é o primeiro passo fundamental para fazer a escolha certa.

Este artigo irá guiá-lo através dos conceitos básicos da capacidade da bateria, dos principais factores que a influenciam e das vantagens e desvantagens dos diferentes tipos de bateria, ajudando-o a selecionar a solução de capacidade e armazenamento de energia mais adequada para cenários de utilização comuns.
O que é a capacidade da bateria?
A capacidade da bateria é um indicador essencial do desempenho da bateria, representando a quantidade total de energia que uma bateria pode libertar em condições específicas, como a taxa de descarga, a temperatura ambiente e a tensão de corte.
A capacidade da bateria é normalmente expressa em três unidades: Ah (Ampere-hora), Wh (Watt-hora) e kWh (Kilowatt-hora):
Ampere-hora (Ah): Mede a corrente que uma bateria pode fornecer numa hora.
Watt-hora (Wh): Mede a energia armazenada, calculada como Wh = Ah × V.
Kilowatt-hora (kWh): 1 kWh = 1.000 Wh, normalmente utilizado para armazenamento doméstico de energia e grandes sistemas de baterias.
Para os consumidores, Wh ou kWh é mais intuitivo, pois reflecte diretamente a quantidade de energia que uma bateria pode armazenar e o tempo que pode alimentar os dispositivos.
Factores que afectam a capacidade da bateria solar
Temperatura ambiente
A maioria das pilhas tem um intervalo de temperatura de funcionamento ideal e temperaturas extremamente altas ou baixas podem afetar a capacidade real.
Alta temperatura: Acelera as reacções químicas internas, o que pode levar a uma degradação mais rápida da capacidade ao longo do tempo.
Baixa temperatura: Abranda a migração do ião de lítio, reduzindo a capacidade útil da bateria.
Em comparação com outros tipos de baterias, as baterias LiFePO4 são mais resistentes à temperatura. Por exemplo, as baterias solares GODE funcionam entre -20°C e 65°C, cobrindo a maioria dos cenários práticos.
Tipo de bateria
O tipo de bateria é um fator chave para determinar a capacidade e a vida útil. Os tipos mais comuns incluem:
Bateria de iões de lítio: Densidade energética elevada, peso leve, ciclo de vida longo e volume mais pequeno para a mesma capacidade, mas ligeiramente menos estável do que o LiFePO4.
Bateria LiFePO4: Alta segurança, vida útil mais longa, adequado para armazenamento doméstico e grandes aplicações ao ar livre.
Bateria de chumbo-ácido: Baixo custo, mas baixa densidade energética, volumoso e com ciclo de vida curto.
Os produtos GODE utilizam baterias LiFePO4, equilibrando a segurança e a longa duração, com ciclos de vida superiores a 6000 ciclos, reduzindo significativamente os custos a longo prazo.
Taxa de carga e descarga
A taxa de carga e descarga afecta diretamente a utilização da capacidade da bateria e o seu tempo de vida. Com taxas de descarga baixas (por exemplo, 0,2C), a migração de iões é suficiente, produzindo uma maior capacidade utilizável. Taxas de descarga elevadas (por exemplo, 1C) aumentam os efeitos de polarização, reduzindo a capacidade útil efectiva.
Do mesmo modo, o carregamento a baixa velocidade reduz a perda de energia e as reacções secundárias, melhorando a capacidade sustentável, enquanto o carregamento a alta velocidade encurta o tempo de carregamento, mas pode acelerar a polarização e as reacções secundárias, afectando a capacidade e a vida útil.
Ciclo de vida
À medida que os ciclos de carga-descarga aumentam, as alterações estruturais nos eléctrodos, a perda de material ativo e a decomposição do eletrólito reduzem gradualmente a capacidade, normalmente medida pelo número de ciclos até que a capacidade desça para 80% do valor inicial.
As baterias GODE excedem normalmente os 6000 ciclos, destacando-se entre produtos semelhantes com uma vida útil mais longa.
Como calcular a capacidade necessária da bateria
Passo 1. Determinar a potência do dispositivo
Verificar a potência (unidade: W) na etiqueta do aparelho. Se apenas forem fornecidas a tensão e a corrente, calcular a potência da seguinte forma Potência (W) = Tensão (V) × Corrente (A).
Por exemplo: Computador portátil Huawei MateBook 13, tensão de entrada 20 V × corrente 3,25 A = 65 W

Passo 2. Estimar o tempo de utilização
Potência do dispositivo × Horas de utilização = Energia necessária (Wh), Para um computador portátil que consome 65 W, o seu funcionamento durante uma hora requer 65 Wh.
Passo 3. Soma total + Margem de reserva
Adicione todos os dispositivos que tenciona utilizar em simultâneo, tenha em conta a potência de arranque e reserve uma capacidade extra de 20-30%.
| Electrodomésticos | Potência de funcionamento | Potência de arranque |
| Ar condicionado | 500 W | 3,000-5,000 W |
| Chaleira eléctrica | 1,800 W | 1,800 W |
| Frigorífico | 100 W | 200 W |
| Máquina de lavar roupa | 300 W | 440 W |
| Micro-ondas | 1,000 W | 1,000 W |
| Secador de cabelo | 2,000 W | 2,000 W |
| Aspirador de pó | 1,000 W | 1,000 W |
| TV | 500 W | 0 |
| Luz LED | 20 W | 0 |
| Telemóvel | 60 W | 0 |
Por exemplo, durante um corte súbito de energia durante a noite, como fonte de energia de reserva, os dispositivos essenciais precisam de ser alimentados.
Por exemplo:
Luz LED:20 W × 5h = 100 Wh
Frigorífico:100 W × 12 h = 1.200 Wh
Telemóvel:60 W × 1 h × 3 = 180 Wh
A procura total é de 1480 Wh, pelo que se recomenda uma bateria de 2100Wh para cobrir uma noite inteira.
Intervalos de referência comuns da capacidade da bateria
Dependendo do cenário de utilização, a capacidade da bateria recomendada para centrais eléctricas portáteis ou baterias solares é aproximadamente a seguinte
| Cenário de utilização | Capacidade recomendada | Notas |
| Telemóveis, tablets | 100-300 Wh | Pode ser carregado várias vezes, é leve e portátil |
| Computadores portáteis pequenos | 300-1.000 Wh | Pode funcionar continuamente durante 4-6 horas |
| Pequeno acampamento ao ar livre | 1-3 kWh | Alimentam luzes, ventoinhas, pequenos aparelhos de cozinha |
| Reserva de emergência doméstica | 3-10 kWh | Alimentam o frigorífico, as luzes, os computadores e os dispositivos de comunicação |
| Backup para toda a casa/longa duração | 10-30 kWh | Alimenta electrodomésticos durante longos períodos de inatividade |
| Armazenamento de energia comercial/industrial | 50 kWh+ | Suporta pequenos escritórios, lojas ou cargas industriais para utilização prolongada |
Ao selecionar uma bateria, considere a procura real de energia + margem de reserva + escalabilidade de forma abrangente.

Em geral, as centrais eléctricas portáteis situam-se entre 0,3 e 3 kWh, os armários domésticos de armazenamento de energia variam tipicamente entre 5 e 30 kWh e o armazenamento de energia para fins comerciais pode atingir mais de 50 kWh.
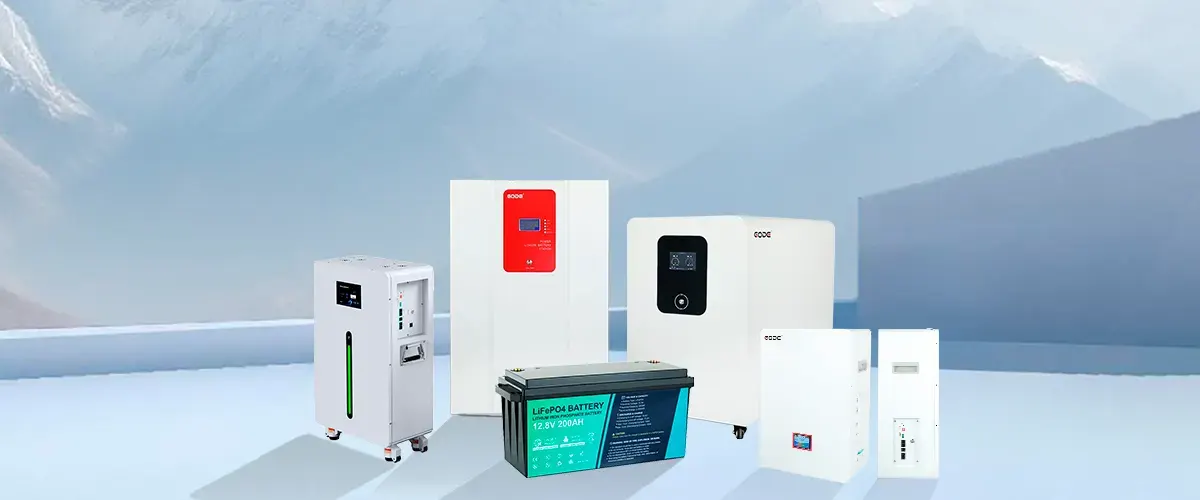
A linha de produtos da GODE é abrangente, cobrindo centrais eléctricas portáteis, energia de reserva em casa, sistemas domésticos de armazenamento de energiae em grande escala armários para armazenamento de energia comercial e industrial. Todas utilizam baterias de fosfato de ferro e lítio (LiFePO4), que oferecem elevada segurança e estabilidade, ciclos de vida longos e a capacidade de satisfazer as suas necessidades de energia em vários cenários.

Como prolongar a vida útil da bateria?
Bons hábitos de carregamento
Evitar o excesso de carga e a descarga profunda: Mantenha o nível da bateria entre 20%-80% e evite carregar até 100% ou descarregar até 0% durante períodos prolongados.
Carregar conforme necessário: Não é necessário esperar até que a bateria esteja totalmente descarregada. O carregamento e o descarregamento superficiais são melhores para a saúde da bateria.
Evitar o carregamento noturno: Se for necessário efetuar um carregamento noturno, active a função "Carregamento optimizado da bateria", que reduz a velocidade de carregamento para evitar o excesso de carga.
Temperatura de funcionamento adequada
A temperatura óptima de funcionamento das baterias situa-se entre 20°C e 30°C. Evite utilizar a bateria em condições de calor ou frio extremos, uma vez que as temperaturas elevadas aceleram o envelhecimento e as temperaturas baixas afectam o desempenho.
Utilizar equipamento de carga original
Utilize carregadores originais ou certificados e evite carregadores de baixa qualidade que podem causar tensão instável e reduzir a vida útil da bateria.
Manutenção regular
A manutenção da saúde da bateria é crucial para prolongar a sua vida útil. Verifique regularmente o nível de carga da bateria, o estado de carga/descarga, a tensão e a temperatura para detetar anomalias e evitar o declínio da capacidade. Além disso, inspeccione a bateria quanto a inchaço, danos ou corrosão. As baterias GODE estão equipadas com um BMS, que monitoriza a bateria
em tempo real, prevenindo eficazmente potenciais riscos de segurança.
Mantenha as portas e a superfície da bateria limpas para evitar que o pó ou a oxidação afectem o desempenho. Com estas medidas de manutenção simples, mas sistemáticas, a sua central eléctrica portátil e a bateria solar permanecerão sempre em óptimas condições.
Conclusão
A capacidade da bateria não é apenas um parâmetro técnico; afecta diretamente o desempenho das baterias solares no mundo real. Desde a compreensão dos conceitos básicos de Ah, Wh e kWh, ao domínio dos factores que influenciam a capacidade da bateria e, finalmente, à seleção da capacidade com base nas necessidades reais - cada passo é crucial para garantir um suporte de energia estável e duradouro.
Quer esteja a preparar-se para comprar uma estação de energia portátil para o exterior ou a considerar uma bateria de grande capacidade para a sua casa ou caravana, a escolha da capacidade correta da bateria é essencial para garantir energia fiável para a vida e para o trabalho. Para tornar o seu equipamento mais duradouro, siga bons hábitos de carga e descarga e efectue uma manutenção regular. Desta forma, a sua bateria não só satisfará as necessidades actuais, como também manterá um funcionamento eficiente durante mais tempo no futuro.
Perguntas frequentes sobre a capacidade da bateria
ação